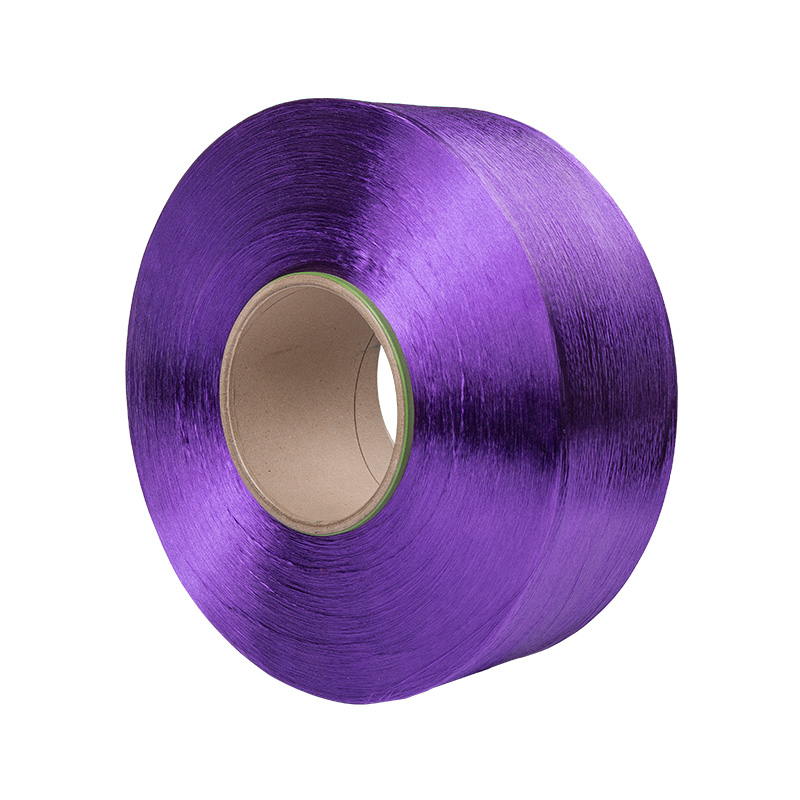
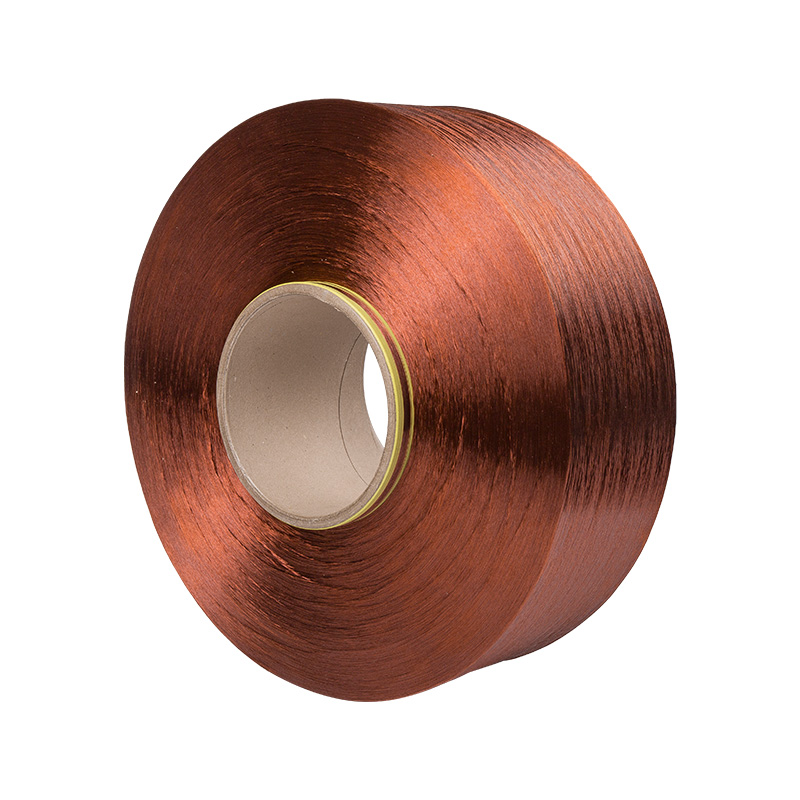
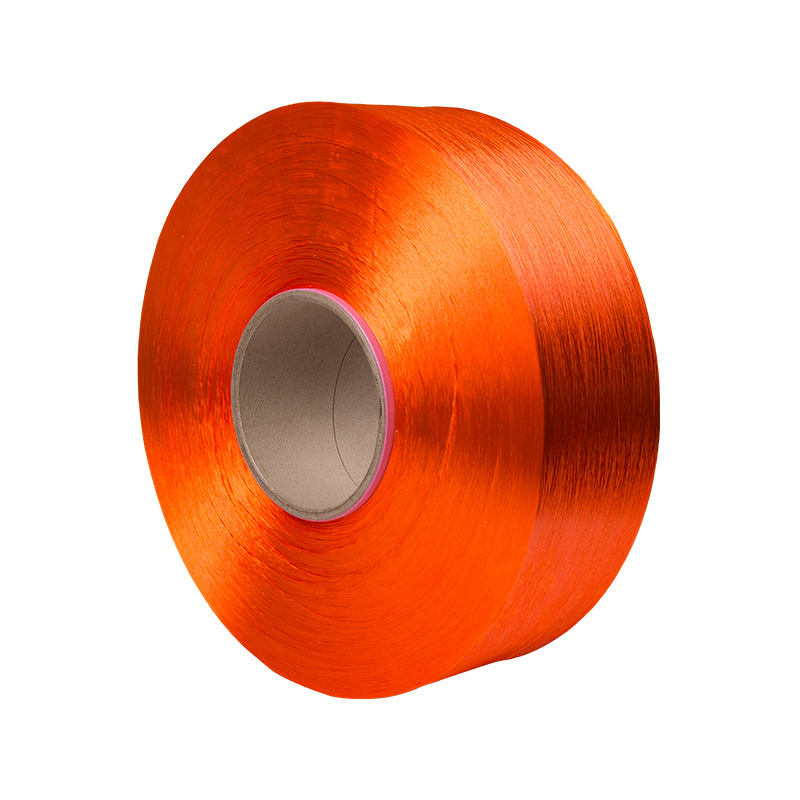
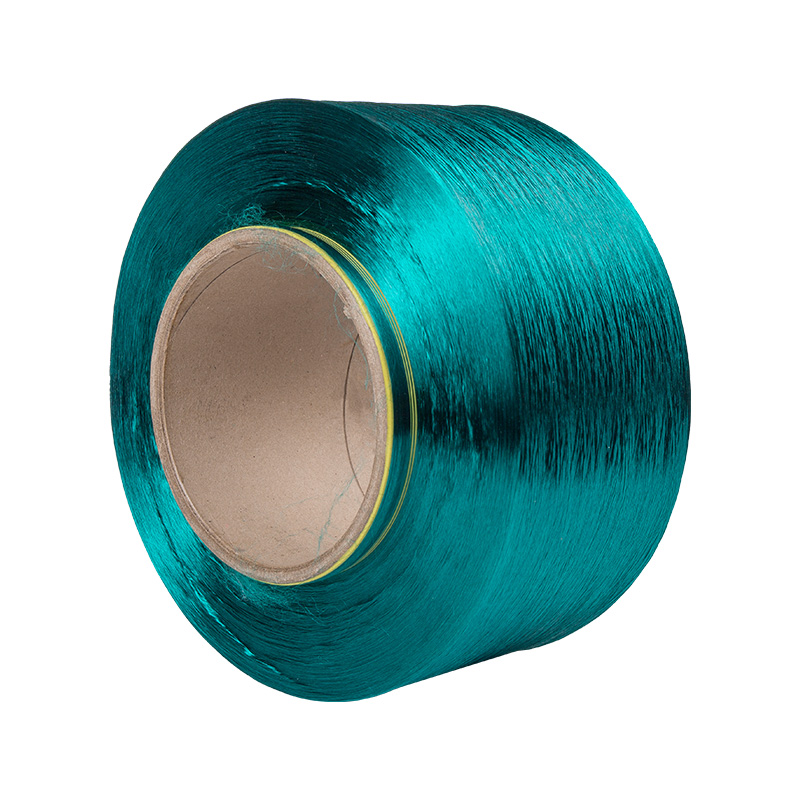
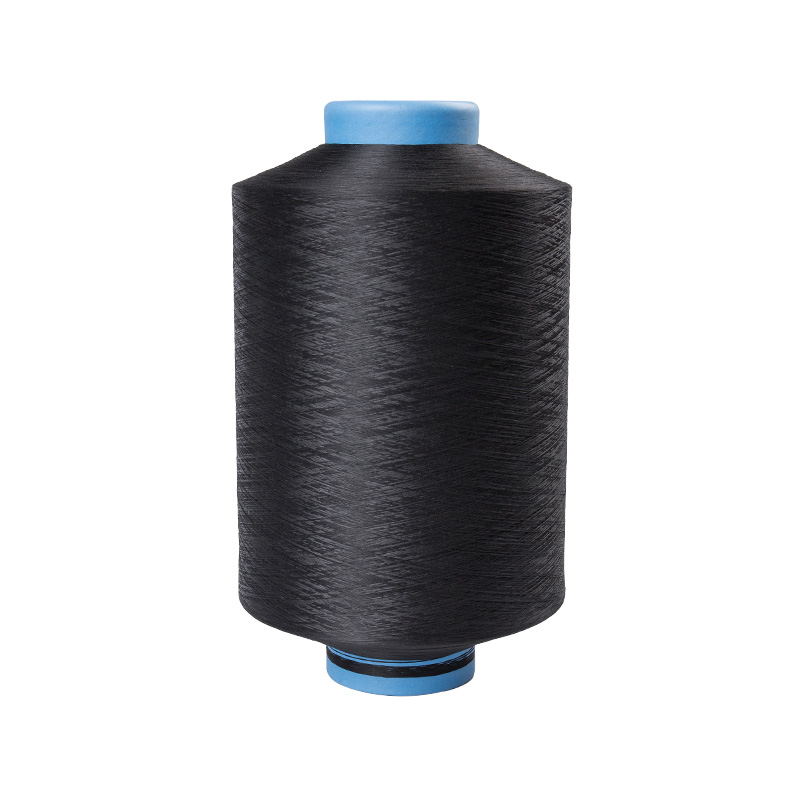
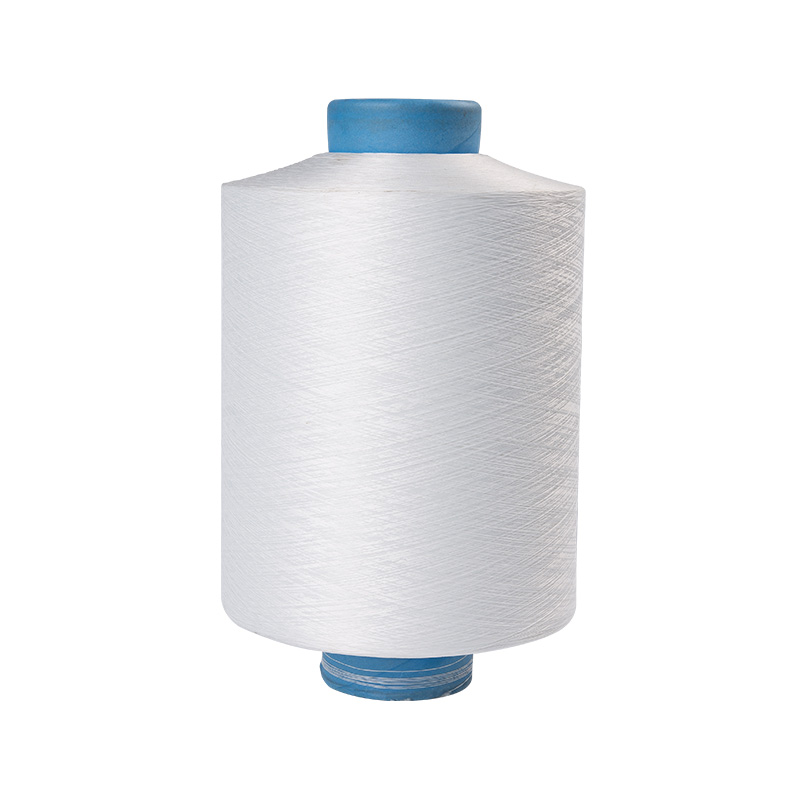
Texturing Spinning Yarn Manufacturers


2010
sinceShuhao
about our story
Shaoxing Shuhao Textile Technology Co., Ltd. was established in 2010. is a China Texturing Spinning Yarn Manufacturers and Texturing Spinning Yarn Factory,It is located in Hangzhou Bay, east of Cao'e River, and located in the north side of Shaoxing Binhai Industrial Zone. The total investment is 300 million yuan. It is a professional manufacturer of high-quality polyester fiber spinning and texturing An integrated chemical fiber enterprise with an annual output of 150,000 tons and an annual export volume of more than 50,000 tons. As a professional spinning and texturing company, the company has a very prominent competitive advantage.
-

-

From pre-sales to manufacture and after-sales, we provide timely support and service to meet your every need.
-
.png)
Customization:
We have a strong R&D team that can develop and produce products according to the samples provided by customers.
-

Cost
We have one-stop production of spinning and texturing, which has advantages in production cost, high quality, and low price.
-
.png)
Quality
We check every thread, and the most advanced testing equipment in the industry ensures product quality.
-

Shipment
We usually ship by sea, not far from Beilun Port, so it is more convenient to ship goods to any other countries.
-
Capacity
Our annual output exceeds 20,000 tons, which can meet the needs of customers with different purchase volumes.
-
.png)
Service
We are based on high-grade and high-end markets, and our products meet international standards, and are exported around the world.
Our Advantages
Polyester fiber spinning and texturing.
Our company has a spinning factory, a texturing factory, and an integrated spandex-covered yarn machine. The main products are colored filament yarn (FDY), POY yarn, low elastic yarn (DTY), network yarn (ACY) spandex coated yarn.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体